Decentralized finance, or DeFi, has been one of the most revolutionary applications in Web 3. So, what is automated market maker, and how does it find a place in this sphere? The advent of decentralized exchanges (DEX) has not just democratized the adoption of cryptocurrency but has also given rise to new and innovative ways to access financial opportunities – Automated Market Maker being one among the many ways that were traditionally never heard of. Yes, now you can do all the major banking activities within the crypto ecosystem minus an intermediary. In a traditional setup, the intermediary, as we all know, retains the unilateral power to choose to serve you or ignore you. However, the tables turn in the case of a decentralized setup, where none alone and all together make up the platform’s ecosystem via peer-to-peer interaction.
This article will help you understand what is Automated Market Maker, i.e., AMM, a fundamental pillar in DeFi – in the most beginner-friendly manner.
Table of Contents
Imagine you’re a farmer wanting to sell your farm produce. Who do you sell to? A buyer. Now imagine you’re somebody who needs to buy some veggies for consumption, i.e., a consumer. Who do you buy from? Yes, that’s right, a seller!
In this scenario, let’s think of a conventional way of successfully completing a transaction. Getting the farm produce to actual consumers would require a great amount of planning and logistics. Packaging, transporting, storage, shipping, and collecting payments require a lot of resources. Apart from these, each of these steps can put a significant financial burden on the farmers.
So how do the farmers sell? This is where the intermediaries come in. The mediators purchase goods in bulk from farmers. They take care of all the intermediate processes, add their cut over the purchase price (hence the concept of ‘markup’), and then sell it to consumers like us.
One of the most important functions of a market maker crypto (or non-crypto) is to provide liquidity. Imagine being a farmer with nobody to sell to or a consumer without purchasing goods! These market makers ensure that there is always a buyer for a farmer to sell their products and a seller to purchase from for a consumer.
Automated market makers are a component of decentralized exchanges (DEXs), which were designed to eliminate the need for any middlemen in the trade of cryptocurrency assets. AMM can be thought of as computer software that automates liquidity provision. Assets are priced using a pricing algorithm rather than an order book as in a traditional exchange.
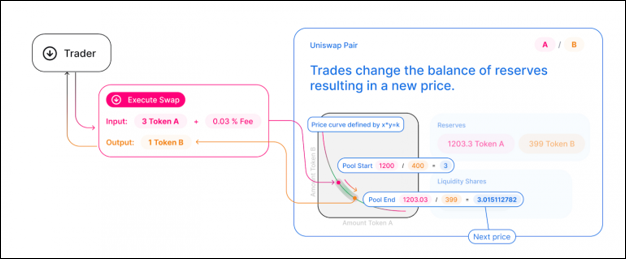
This formula may differ depending on the protocol. Uniswap, for example, employs x * y = k, where x represents the amount of one token in the liquidity pool and y represents the amount of the other. In this formula, k is a fixed constant, which means that the total liquidity of the pool must always remain constant. The value of Asset A is represented by x, and the value of Asset B is represented by y. In essence, the Uniswap liquidity pools always maintain a state in which the multiplication of the prices of Assets A and B equals the same number.
These protocols define the price of digital assets and provide liquidity by utilizing smart contracts, which are self-executing computer programmes. The protocol pools liquidity into smart contracts in this case. In essence, users are not trading against counterparties but rather against the liquidity locked inside smart contracts. These smart contracts are frequently referred to as liquidity pools.
Trade in the AMM protocol does not require the participation of another trader. Instead, you can use a smart contract to trade. As a result, trades are peer-to-contract rather than peer-to-peer. You must find an individual ETH/USDT liquidity pool if you want to trade one crypto asset for another, such as Ether (Ethereum’s native currency) for Tether (Ethereum token pegged to the US dollar).
Anyone with an internet connection and ERC-20 tokens of any type can become a liquidity provider by contributing tokens to an AMM’s liquidity pool. For providing tokens to the pool, liquidity providers typically earn a fee. Traders who interact with the liquidity pool must pay this fee.

Below summarizes the ‘constant product’ formula incorporated in AMMs.
x*y = k
Where,
‘x’ is the number of token 1 within the pool, ‘y’ is the number of token 2 within the pool & ‘k’ is a constant.
This “k” stays constant and changes only when liquidity is withdrawn from the pool.
How are these pools created?
This is where the power of Web 3 kicks in by allowing anyone to participate in a permissionless manner. Any user with some extra crypto tokens can provide liquidity to the AMMs, i.e., they can add tokens to the pool in proportions based on the constant for the chosen trading pair (e.g., ETH/USDT), and they can further earn some crypto tokens in exchange.
Let’s take an example of the ETH/USDT pair to understand the above concept further.
Imagine a pool with 10,000 USDT and 5 ETH (figures taken only for calculation and understanding purposes)
k= x*y and in this case, k= 10,000 * 5= 50,000
If a seller wishes to sell 1 ETH to this pool, the amount of ETH would rise to 6. Now, to keep ‘k’ constant, the amount of USDT in this pool should decrease to 50,000/6 = 8333.33. Thus, the seller will receive 10,000 – 8333.33 = 1666.67 USDT in exchange of 1ETH. Similarly, if a buyer wishes to exchange, say 1000 USDT for some ETH, a similar calculation would be made in order to maintain the value of the ‘k’ constant.
Keep in mind, unlike the order book matching process we have been accustomed to in stock brokerage platforms and exchanges, the buy/sell transactions and the settlements are cleared instantly with the help of much higher levels of automation, i.e., smart contracts, as mentioned previously.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts between two parties triggered when preset conditions are met. And the preset conditions are based on prediction markets. Although what is automated market maker is that it removes the necessity for an intermediary. Prediction markets can’t be deemed perfect, but innovations in this field based on better models have helped AMMs to improve over the last six years since the Reddit post by Vitalik Buterin proposing what AMM is in crypto.
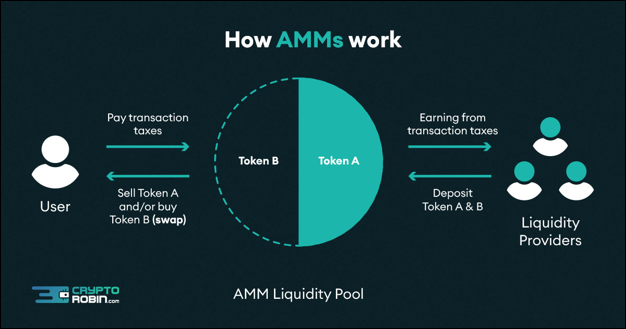
Before AMMs or automated maker crypto, order books were essential for trading. People could offer various rates for buying and selling assets on traditional market platforms.
But what does AMM in crypto do? It is a mechanism used in DeFi to create liquidity.
Liquidity refers to how quickly an asset may be purchased and sold. A high level of liquidity indicates that the market is busy and that many traders are buying and selling a specific item. In contrast, low liquidity results in less activity and makes buying and selling assets more difficult. Slippages frequently happen when liquidity is limited. In other words, before a trade is closed, the price of an asset at the time of execution changes significantly.
DEXs, using AMM in crypto, help to make it possible for digital assets to be traded automatically. They accomplish this by substituting liquidity pools for conventional buyer and seller markets.
Automated market maker crypto – has gained acceptance very rapidly. AMM can be thought of as a tool that facilitates trades between two assets at a reasonable market price. AMM can be compared to computer software that streamlines the provision of liquidity. These protocols use smart contracts, a type of self-executing computer code, to establish the price of cryptocurrency tokens and offer liquidity.
You can make trades using the AMM protocol without the assistance of another trader. Instead, you use a smart contract for trading using a market maker. Crypto Trading is, therefore, a peer-to-contract rather than just a peer-to-peer transaction.
It’s crucial to understand two facts concerning AMMs:
Individual “liquidity pools” for trading pairs that you typically see on a centralized exchange exist in AMMs. You must locate a unique ETH/USDT liquidity pool if you wish to exchange one cryptocurrency for another, such as Ether (Ethereum’s native currency) for Tether (Ethereum token tied to the US dollar).
By depositing both of the assets represented in the pool, anyone can supply liquidity to these pools in a place by hiring specialized market makers. For instance, you would need to deposit a specific fixed ratio of ETH and USDT if you wanted to become a liquidity provider for an ETH/USDT pool.
Since the spot price of the tokens is always along the curve defined by x*y = k, there can be instances where the price on a DEX is lesser than the market price. This potentially gives rise to an arbitrage opportunity where a trader can buy/sell from the market and exchange the tokens from the liquidity pools with larger spreads. Thus, AMM in crypto effectively incentivizes the traders to maintain the balance between tokens and the constant ‘k.’
When a participant adds liquidity to the AMM protocol, they receive LP tokens in exchange. These LP tokens can be burned to get back the tokens added initially. However, one of the biggest advantages of these LPs is that they can also be staked. Staking unlocks passive earning opportunities as it facilitates earning interest income. You can also redeem your LP tokens when you want to, although some DEXs may charge small fees if you redeem them too early.
Slippages occur when the price quoted by the DEX changes – from the time of quote to the time of swap. The AMMs typically provide the facility to set the slippage limits. This helps traders to limit their slippages and gain more control over their transactions.
As the liquidity pools such as those in Uniswap operate in a ‘constant product’ curve, there can be cases where the ratio of the initial supply will change after you add the tokens. This leads to an impermanent loss until the ratio of tokens returns to where you invested.
The loss, however, becomes permanent only when you withdraw your tokens. Let me break this down and simplify what an impermanent loss is. So let’s say you have $1000 worth of BTC in June 2022. In August 2022, the BTC price went down, and the BTC value in your portfolio now amounts to $800. As of August 2022, your impermanent loss is $200. In this scenario, impermanent losses are not permanent unless you wish to sell them for a loss.
Automated market maker crypto enables a larger spectrum of investors to trade cryptocurrencies because they work within a decentralized exchange. With AMM coin exchanges, anyone with a crypto wallet can trade digital currencies. AMMs in crypto also allows anyone to become a liquidity provider, which comes with incentives. Liquidity providers get a fraction of the fees paid on transactions executed on the pool.
Source: 101 Blockchains | AMM augments the liquidity pool
As long as traders are willing to operate as liquidity providers, Automated market maker crypto can provide more liquidity than traditional market makers. AMM helps set up a system of liquidity where anyone can contribute to it. This removes any intermediary lowering transaction fees for investors. High liquidity is essential for healthy trading activity.
If there is less liquidity, it could cause slippage. Low liquidity introduces high volatility in the prices of assets in the market. Slippage is the term for pricing discrepancies that might happen in the presence of weak trading volume and liquidity. Automated market makers can contribute to more liquidity creation, which lowers slippage.
As the DeFi ecosystem grows, you can expect more innovations in the upcoming years to help you access various financial opportunities. The core principle of crypto and Web3, in general, is to empower individuals to be their banks. The AMMs will do their part in creating utilities to provide you or anyone with permissionless access to finance beyond boundaries. The future with decentralization is very exciting!
One of the most important functions of a market maker is to provide liquidity. Imagine being a farmer with nobody to sell to or a consumer without purchasing goods! The intermediaries are the market makers who ensure that there is always a buyer for a farmer to sell their products and a seller to purchase from for a consumer. They will take care of everything in between, including logistics, and they provide this service for a fee.
As you can imagine, instead of intermediaries, AMM, i.e., market maker crypto, is done with the help of automation via smart contracts. There is also an incentive for consumers or traders, in this case, to make sure there is enough liquidity in the market.
Traders can find incentives in the form of age-old arbitrage and slippage opportunities. Further, compared to the fees charged by an intermediary in the Web 2 world, decentralized exchanges or DEXs who use AMM charge very low fees. And note, regardless of whether you are a new DeFi/crypto user or living out of an impoverished nation, you can use DeFi services to earn passive income and make financial transactions for a living.
An automated market maker in cryptocurrency presents various opportunities and threats for a user or an investor, such as arbitrages, interest-yielding deposit/savings plans, slippages, and impermanent losses. Here, the threats are not threats per se unless you haven’t done enough research about a liquidity pair or any product in the crypto ecosystem before investing or playing a role as a liquidity provider (LP). If used wisely, you can earn passive income and earn profits from arbitrages consistently.
What is Fiat Currency | What is Distributed Ledger Technology | What is Staking Crypto | What are EVM Compatible Blockchains | Different Types of Nodes in Blockchain | What are Whales in Crypto | Crypto Metaverse | Can the Blockchain be Hacked | Benefits of Blockchain | What does Proof of Stake Mean | Cloud Mining Platform | What is POW in Cryptocurrency | Types of Altcoins | Mobile App Technology Stack | How Does Blockchain Wallet Work | Main Features of Blockchain | Blockchain Technology Stocks | What are Layer 1 Blockchain | Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain Technology | What is Miner Extractable Value
Opinions expressed and the content in this publication are those of the author(s). They do not necessarily purport to reflect the opinions or views of Shardeum Foundation.
About the Author : Yash Nair is a product manager on the weekdays and a cinephile over the weekends. He is curiously exploring Web 3.0 and all things crypto. You can follow him on Twitter